What is a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve
A pneumatic solenoid valve is an electromechanical device used to control airflow in automated systems. By energizing or de-energizing its electromagnetic coil, it directs compressed air to actuate pneumatic components like cylinders, valves, and actuators. Widely used in industrial automation, solenoid valves ensure precise control of airflow direction, on/off functions, and flow regulation.
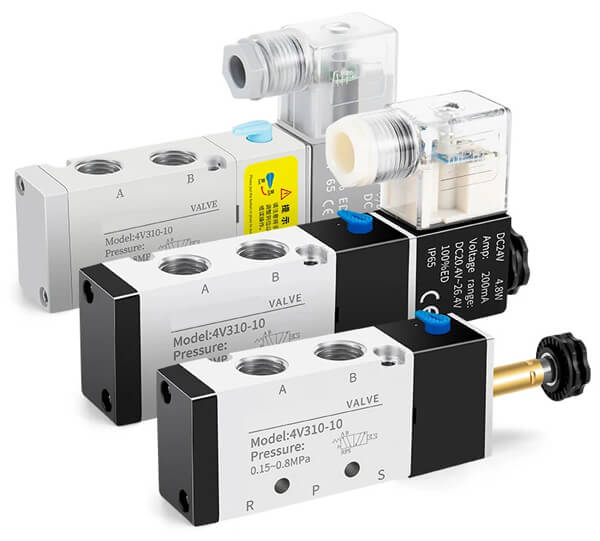

Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Product Overview
A solenoid valve is a core component in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. It regulates fluid flow direction, enabling machinery operation in factories and industrial settings. For example, it controls hydraulic/pneumatic cylinders to drive mechanical movements.
How Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Work
Inside a pneumatic solenoid valve, a sealed chamber contains multiple ports connected to air tubes. A central valve disc is flanked by two electromagnets. When one coil is energized, the disc shifts to block or open specific ports, redirecting compressed air to drive actuators (e.g., cylinder pistons). The constant open inlet port allows high-pressure air to flow into designated outlets, enabling precise mechanical control.
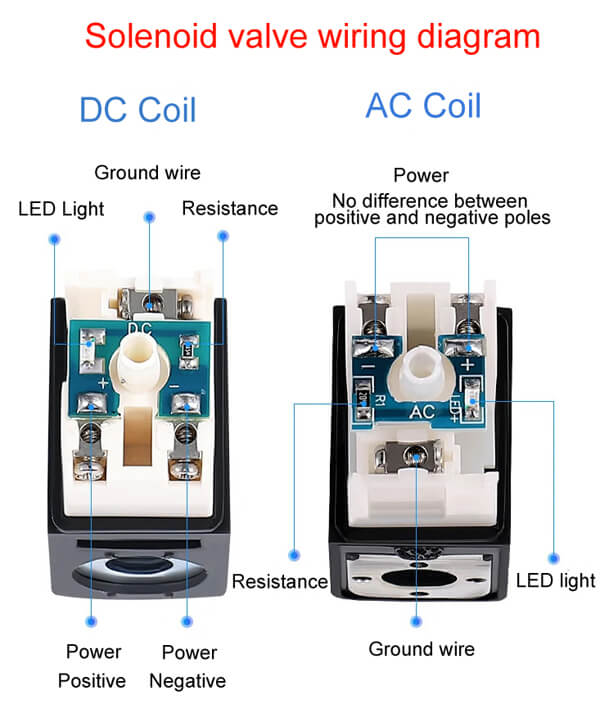
Solenoid Valve Wiring Diagram
Types of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Pneumatic solenoid valves are categorized by:
1. Working Principle: Direct-acting or pilot-operated valves.
2. Port Configuration: 2-way 2-port, 2-way 3-port, 3-way 5-port (for diverse applications).
3. Voltage: DC24V, AC220V, etc.
4. Special Features: Explosion-proof, waterproof, low-power models.
Key Applications in Industrial Automation
- Direction Control: Manage cylinder extension/retraction.
- Flow On/Off: Act as switches for pneumatic circuits.
- Flow Regulation: Adjust airflow volume (specific models).
Common Valves Using Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves are important components for controlling the opening and closing of pneumatic valves and are usually used for the following valves:
- Pneumatic Gate Valves
- Control Valves
- Pneumatic Globe Valve
- ESDV (Emergency Shutdown Valves)
Pneumatic accessories
The Pneumatic accessories includes:
1. Filter-Regulator: Cleans air by removing moisture and stabilizes pressure.
2. Solenoid Valve: Controls airflow to valves/actuators.
3. Limit Switch: Monitors valve position (open/close status).
Pro Tip:
- 3/2-way solenoid valves pair with spring return pneumatic actuators.
- 5/2-way solenoid valves suit double-acting pneumatic actuators.
How to Choose a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve
1. Environment: Consider temperature, pressure, and gas type (air, fuel).
2. Type & Structure: Direct-acting vs. pilot-operated; single/double-seat designs.
3. Technical Specs: Pressure rating, response time, leakage rate, and explosion-proof ratings.
4. Power & Operation: Match voltage (DC24V/AC220V); manual/auto/remote control.
5. Brand & Certification: Opt for ISO-certified brands for reliability.
6. Cost-Efficiency: Prioritize quality over low prices.

FESTO Brand Solenoid Valves
IP Ratings for Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Common IP ratings (Ingress Protection):
- IP65: Dustproof + water jet resistance.
- IP66/IP67: Dustproof + water immersion resistance.
- IP68: Dustproof + prolonged submersion protection.
Explosion-Proof Ratings (IEC Standards)
Key **explosion-proof ratings** for hazardous environments:
- Exd: Flameproof (oil/gas industries).
- Exe: Increased safety (mining, railways).
- Exia: Intrinsic safety (low-energy ignition prevention).
- Exp/Exo/Exq: Specialized protection (pressurized/oil-filled/sand-filled designs).
Post time: Mar-29-2025

